Hackerrank Java Arraylist Solution

.MathJax_SVG_LineBox {display: table!important} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox span {display: table-cell!important; width: 10000em!important; min-width: 0; max-width: none; padding: 0; border: 0; margin: 0}
Sometimes it's better to use dynamic size arrays. Java's Arraylist can provide you this feature. Try to solve this problem using Arraylist.
You are given lines. In each line there are zero or more integers. You need to answer a few queries where you need to tell the number located in position of line.
Take your input from System.in.
Input Format
The first line has an integer . In each of the next lines there will be an integer denoting number of integers on that line and then there will be space-separated integers. In the next line there will be an integer denoting number of queries. Each query will consist of two integers and .
Constraints
Each number will fit in signed integer.
Total number of integers in lines will not cross .
Output Format
In each line, output the number located in position of line. If there is no such position, just print "ERROR!"
Sample Input
5
5 41 77 74 22 44
1 12
4 37 34 36 52
0
3 20 22 33
5
1 3
3 4
3 1
4 3
5 5
Sample Output
74
52
37
ERROR!
ERROR!
Explanation.MathJax_SVG_LineBox {display: table!important} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox span {display: table-cell!important; width: 10000em!important; min-width: 0; max-width: none; padding: 0; border: 0; margin: 0}
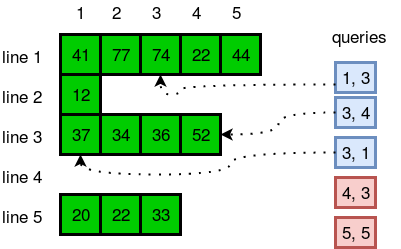
The diagram below explains the queries:
Solution in java8
Approach 1.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String s = sc.nextLine();
ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> a = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
s = sc.nextLine();
a.add(i, new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(s.split("\\s"))));
}
int m = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
if (x <= a.size() && y < a.get(x-1).size() && y >= 0) {
System.out.println(a.get(x-1).get(y));
} else {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
}
}
}
}Approach 2.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
List<List<Integer>> matrix = new ArrayList();
Stream.iterate(0, x -> x + 1).limit(scan.nextInt()).forEach(x -> {
final List<Integer> line = new ArrayList();
Stream.iterate(0, y -> y + 1).limit(scan.nextInt()).forEach(y -> {
line.add(scan.nextInt());
});
matrix.add(line);
});
Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 1).limit(scan.nextInt()).forEach(n -> {
try {
System.out.println(matrix.get(scan.nextInt() - 1).get(scan.nextInt() - 1));
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
}
});
}
}Approach 3.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = input.nextInt();
List<List<Integer>> A = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int l = input.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(l-- > 0) {
a.add(input.nextInt());
}
A.add(a);
}
int m = input.nextInt();
while(m-- > 0) {
int line = input.nextInt()-1;
int position = input.nextInt()-1;
if (line >= A.size()) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
} else if (position >= A.get(line).size()) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
} else {
System.out.println(A.get(line).get(position));
}
}
}
}