Hackerrank Breadth First Search: Shortest Reach Solution

.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox {display: table!important} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox span {display: table-cell!important; width: 10000em!important; min-width: 0; max-width: none; padding: 0; border: 0; margin: 0}
Consider an undirected graph where each edge is the same weight. Each of the nodes is labeled consecutively.
You will be given a number of queries. For each query, you will be given a list of edges describing an undirected graph. After you create a representation of the graph, you must determine and report the shortest distance to each of the other nodes from a given starting position using the breadth-first search algorithm (BFS). Distances are to be reported in node number order, ascending. If a node is unreachable, print for that node. Each of the edges weighs 6 units of distance.
For example, given a graph with nodes and edges, , a visual representation is:
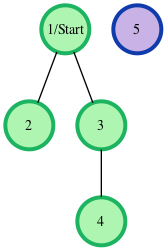
The start node for the example is node . Outputs are calculated for distances to nodes through : . Each edge is units, and the unreachable node has the required return distance of .
Function Description
Complete the bfs function in the editor below. It must return an array of integers representing distances from the start node to each other node in node ascending order. If a node is unreachable, its distance is .
bfs has the following parameter(s):
- n: the integer number of nodes
- m: the integer number of edges
- edges: a 2D array of start and end nodes for edges
- s: the node to start traversals from
Input Format.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox {display: table!important} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox span {display: table-cell!important; width: 10000em!important; min-width: 0; max-width: none; padding: 0; border: 0; margin: 0}
The first line contains an integer , the number of queries. Each of the following sets of lines has the following format:
- The first line contains two space-separated integers and , the number of nodes and edges in the graph.
- Each line of the subsequent lines contains two space-separated integers, and , describing an edge connecting node to node .
- The last line contains a single integer, , denoting the index of the starting node.
Constraints.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue}
Output Format.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue}
For each of the queries, print a single line of space-separated integers denoting the shortest distances to each of the other nodes from starting position . These distances should be listed sequentially by node number (i.e., ), but should not include node . If some node is unreachable from , print as the distance to that node.
Sample Input.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue}
2
4 2
1 2
1 3
1
3 1
2 3
2
Sample Output.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue}
6 6 -1
-1 6
Explanation.MathJax_SVG_Display {text-align: center; margin: 1em 0em; position: relative; display: block!important; text-indent: 0; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; width: 100%} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace {font-family: monospace} .MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif {font-family: sans-serif} .MathJax_SVG {display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; line-height: normal; font-size: 100%; font-size-adjust: none; text-indent: 0; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0; min-height: 0; border: 0; padding: 0; margin: 0} .MathJax_SVG * {transition: none; -webkit-transition: none; -moz-transition: none; -ms-transition: none; -o-transition: none} .mjx-svg-href {fill: blue; stroke: blue} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox {display: table!important} .MathJax_SVG_LineBox span {display: table-cell!important; width: 10000em!important; min-width: 0; max-width: none; padding: 0; border: 0; margin: 0}
We perform the following two queries:
- The given graph can be represented as:
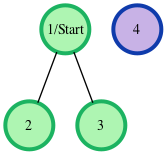
where our start node, , is node . The shortest distances from to the other nodes are one edge to node , one edge to node , and an infinite distance to node (which it's not connected to). We then print node 's distance to nodes , , and (respectively) as a single line of space-separated integers: 6, 6, -1.
- The given graph can be represented as:
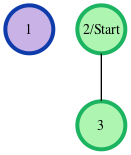
where our start node, , is node . There is only one edge here, so node is unreachable from node and node has one edge connecting it to node . We then print node 's distance to nodes and (respectively) as a single line of space-separated integers: -1 6.
Note: Recall that the actual length of each edge is , and we print as the distance to any node that's unreachable from .
Solution in java8
Approach 1.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static class Graph{
public int N = 0;
public boolean matrix[][];
public Graph(Scanner s){
N = s.nextInt();
int e = s.nextInt();
matrix = new boolean [N][N];
for(int i=0;i <e; i++){
int a = s.nextInt()-1;
int b = s.nextInt()-1;
matrix[a][b] = true;
matrix[b][a] = true;
}
}
public int[] getDistanceToEdges(int s){
boolean visited[] = new boolean[N];
int resp[] = new int[N];
Arrays.fill(resp, 0, N, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(s-1);
resp[s-1] = 0;
visited[s-1]=true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int node = q.poll();
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
if(matrix[node][i] == true){
resp[i] = Math.min(resp[i], resp[node]+1);
if(visited[i]==false){
visited[i]= true;
q.add(i);
}
}
}
}
return resp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int Q = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i< Q;i++){
Solution.Graph g = new Solution.Graph(scanner);
for(int d: g.getDistanceToEdges(scanner.nextInt())){
if (d!=0){
System.out.print(""+((d==Integer.MAX_VALUE)?-1: d*6)+" " );
}
};
System.out.println("");
}
//------
}
}Approach 2.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BreadthFirstSearch {
private Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
private int[][] graph;
private int[] distance;
private boolean[] explored;
private int n, m;
public BreadthFirstSearch(int n, int m) {
this.n = n;
this.m = m;
graph = new int[n][n];
distance = new int[n];
explored = new boolean[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int q = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
BreadthFirstSearch bfs = new BreadthFirstSearch(n, m);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int u = scanner.nextInt() - 1;
int v = scanner.nextInt() - 1;
bfs.graph[u][v] = 1;
bfs.graph[v][u] = 1;
}
int s = scanner.nextInt() - 1;
shortest_reach(bfs, s);
}
}
private static void shortest_reach(BreadthFirstSearch bfs, int s) {
bfs.explored[s] = true;
bfs.queue.add(s);
while (!bfs.queue.isEmpty()){
int v = bfs.queue.remove();
for (int i = 0; i < bfs.n; i++) {
if (bfs.graph[v][i] == 1 && !bfs.explored[i]){
bfs.explored[i] = true;
bfs.queue.add(i);
bfs.distance[i] = bfs.distance[v] + 6;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < bfs.n; i++) {
if (i == s)
continue;
if (bfs.explored[i])
System.out.print(bfs.distance[i] + " ");
else
System.out.print("-1 ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Approach 3.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
private static Map<Integer, List<Integer>> buildGraph(int numNodes, int[][] edges){
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 1; i <= numNodes; i++){
graph.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] edge : edges){
graph.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
graph.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
return graph;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Enter your code here. Read input from STDIN. Print output to STDOUT. Your class should be named Solution. */
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int numQ = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= numQ; i++){
int numNodes = sc.nextInt();
int numEdges = sc.nextInt();
int[][] edges = new int[numEdges][2];
for(int j = 0; j < numEdges; j++){
edges[j][0] = sc.nextInt();
edges[j][1] = sc.nextInt();
}
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = buildGraph(numNodes, edges);
int source = sc.nextInt();
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] res = new int[numNodes+1];
Arrays.fill(res, numNodes);
res[source] = 0;
q.offer(source);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int curNode = q.poll();
for(int neighbor : graph.get(curNode)){
if(res[neighbor] > res[curNode] + 1){
res[neighbor] = res[curNode] + 1;
q.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
for(int j = 1; j <= numNodes; j++){
if(j != source){
System.out.print((res[j] == numNodes ? -1 : res[j]*6) + " ");
}
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}Solution in python3
Approach 1.
import queue
t = int(input())
for i in range(t):
v, e = map(int, input().split())
l = [[0 for x in range(v)] for y in range(v)]
visited = [0 for x in range(v)]
distance = [-1 for x in range(v)]
q = queue.Queue()
for j in range(e):
a, b = map(int, input().split())
l[a - 1][b - 1] = l[b - 1][a - 1] = 1
s = int(input())
q.put(s - 1)
visited[s - 1] = 1
distance[s - 1] = 0
while not q.empty():
a = q.get()
for j in range(v):
if l[a][j] and not visited[j]:
q.put(j)
visited[j] = 1
distance[j] = distance[a] + 6
for j in range(v):
if j != s - 1:
print(distance[j], end = ' ')
print()
Approach 2.
from collections import deque
EDGE_LEN = 6
def print_distances(distances, start):
# print distances
l = []
for d in distances[1:]:
if d != 0:
l.append(str(d))
print(' '.join(l))
def shortest_paths(graph, start):
distances = [-1]*(len(graph))
distances[start] = 0
on_deck = deque()
on_deck.append(start)
while len(on_deck):
curr = on_deck.popleft()
curr_dist = distances[curr] + EDGE_LEN
if graph[curr]:
for node in graph[curr]:
if distances[node] < 0:
distances[node] = curr_dist
on_deck.append(node)
print_distances(distances, start)
num_queries = input()
for _ in range(int(num_queries)):
num_nodes, num_edges = map(int, input().split())
graph = [None]*(num_nodes + 1)
for _ in range(num_edges):
one, two = map(int, input().split())
if graph[one] is None:
graph[one] = set()
if graph[two] is None:
graph[two] = set()
graph[one].add(two)
graph[two].add(one)
s = input()
shortest_paths(graph, int(s))Approach 3.
#!/bin/python3
import sys
from queue import Queue
class Node():
def __init__(self):
self.distance = -1
self.children = []
self.visited = False
def bfs(n, m, edges, s):
nodes = [Node() for _ in range(n)]
for edge in edges:
first, second = [nodes[i - 1] for i in edge]
first.children.append(second)
second.children.append(first)
top = nodes[s - 1]
top.distance = 0
queue = Queue()
queue.put(top)
while(not queue.empty()):
node = queue.get()
for child in node.children:
if (not child.visited) or (child.distance > node.distance + 6):
child.distance = node.distance + 6
child.visited = True
queue.put(child)
del nodes[s - 1]
return [node.distance for node in nodes]
if __name__ == "__main__":
q = int(input().strip())
for a0 in range(q):
n, m = [int(x) for x in input().strip().split(' ')]
edges = []
for edges_i in range(m):
edges_t = [int(edges_temp) for edges_temp in input().strip().split(' ')]
edges.append(edges_t)
s = int(input().strip())
result = bfs(n, m, edges, s)
print (" ".join(map(str, result)))
Solution in cpp
Approach 1.
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<list<int> > g(n);
while(m--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
--a, --b;
g[a].push_front(b);
g[b].push_front(a);
}
int s;
cin >> s;
--s;
vector<int> dist(n, -1);
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
q.push(make_pair(s, 0));
while(!q.empty()) {
pair<int, int> p = q.front();
q.pop();
if(dist[p.first] == -1) {
dist[p.first] = p.second * 6;
while(!g[p.first].empty()) {
q.push(make_pair(g[p.first].front(), p.second + 1));
g[p.first].pop_front();
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
if(i != s)
cout << dist[i] << (i == n-1 ? "\n" : " ");
}
return 0;
}
Approach 2.
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void bfs(int s, vector<vector<int>> graph, int N){
queue<int> qu;
qu.push(s);
vector<int> distance(N,-1);
vector<bool> visited(N,false);
visited[s] = true;
distance[s] = 0;
while(!qu.empty()){
auto node = qu.front();
qu.pop();
for(auto it = graph[node].begin(); it!=graph[node].end(); it++){
if(!visited[*it]){
distance[*it] = distance[node] + 1;
qu.push(*it);
visited[*it] = true;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<N; i++){
if(visited[i] == false)
cout<<-1<<" ";
else if(distance[i]>0)
cout<<distance[i]*6<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int T;
cin>>T;
for(int i = 0; i<T; i++){
int N,M;
cin>>N>>M;
vector<vector<int>> graph(N,vector<int>());
for(int i = 0; i<M; i++){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
graph[n-1].push_back(m-1);
graph[m-1].push_back(n-1);
}
int s;
cin>>s;
bfs(s-1, graph,N);
}
return 0;
}
Approach 3.
// CP template
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
int index; // vertex index
int color; //white = 0, grey =1, black = 2
int dist ; // distance from root
int parent; // vertex's parent
vector<int> edge; // list of vertex connected to vertex
}vertex;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int i=1; i<=T; i++){
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
// set adjacency list
vector<vertex> G(n+1);
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
G[i].index = i;
G[i].color = 0;
G[i].dist = -1;
G[i].parent = -1;
}
// get graph
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
int a,b;
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
G[a].edge.push_back(b);
G[b].edge.push_back(a);
}
int start;
scanf("%d",&start);
// set root
G[start].color = 1;
G[start].dist = 0;
queue<vertex> Q;
Q.push(G[start]);
//printf("a\n");
while(Q.size()){
vertex current = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(int i=0; i<current.edge.size(); i++){
if(G[current.edge[i]].color == 0){
G[current.edge[i]].color = 1;
G[current.edge[i]].dist = current.dist + 6;
G[current.edge[i]].parent = current.index;
Q.push(G[current.edge[i]]);
}
}
G[current.index].color = 2;
}
for(int j=1; j<n; j++){
if(j != start)
printf("%d ",G[j].dist);
}
if(n != start)
printf("%d\n",G[n].dist);
}
return 0;
}
